RFID Solution Designed for the Tire Industry
Tires with embedded RFID tags will change
the tire business history.
Our aim is to help enable a circular economy for the tire industry, contributing to the efficiency of tire-related businesses throughout the supply chain (in manufacturing, distribution, sales, repairs, etc.) by producing RFID tags that can be embedded into automobile tires.

Use cases of RFID-embedded tires
When used with an industry-standard data format, RFID-embedded tires are expected to be utilized in various scenes.
-
Logistics, inventory management
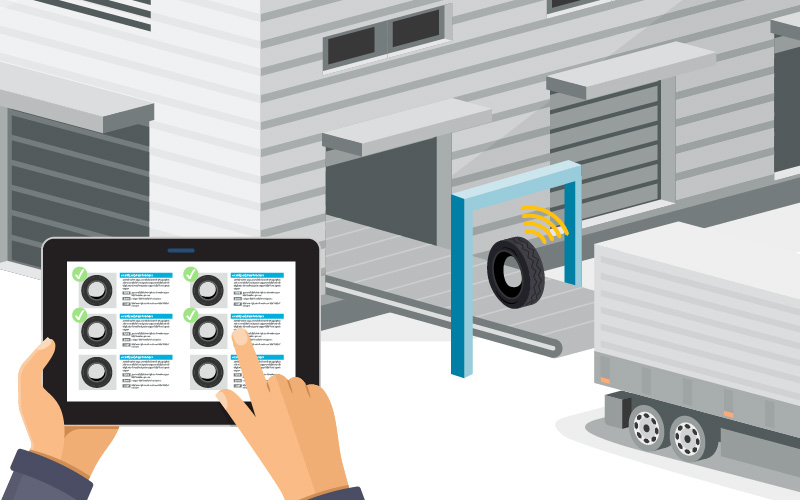

- The RFID tag significantly reduces the workload required to inspect incoming and outgoing tire shipments, as well as to take an inventory of tires.
- Since RFID readings can be updated or shared across different locations in real time, it is also effective at visualizing the status of delivery of tires as well.
-
Automobile production line
- It prevents a new car from having an improper mix of incoming tires or from having such tires mounted in the wrong position.
- Recording such data as manufacturing dates, lots and expiration dates, makes it easier to identify which tires have been recalled.
-
Tire/wheel combination
- It allows the tire and wheel/TPMS combination to be easily tuned. It can also be used effectively in confirming the quality of tires being shipped.
-
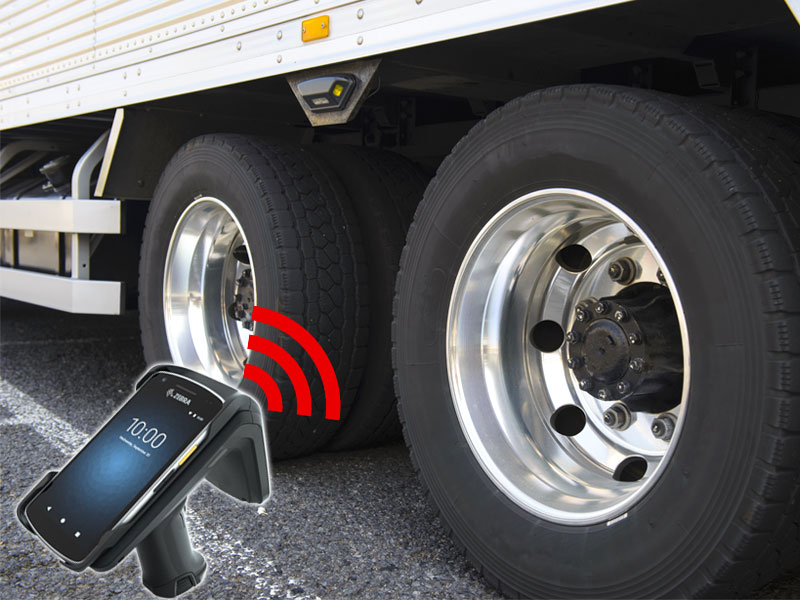
Vehicle tire check
- Checking the tire air pressure and tread depth remaining and keeping a record of the tires mounted on vehicles in a paperless manner lighten the workload for on-site workers.
-
Retread

- Tire product information necessary for tire retreading can be obtained from RFID tags, and retreading applications can be recorded without fail.
-
Checking of tires to be disposed of
- It helps to efficiently keep track of any potential scrap tires while marking them as retreading, recycling, disposal, etc., and encourages them to be reused in an environmentally sound way.
Industry standard-based initiatives
In line with industry-standard systems, we seek to launch and carry out initiatives that will promote "Connected Tires."
ISO-based standardization
It is recommended that the RFID communication standard be RAIN RFID operating at the UHF (860 MHz to 960 MHz) band and the RFID data format used for tires be GS1 SGTIN-96. Tire-embeddable tag is encoded with an SGTIN-96 that functions as tire ID, and tire product information is stored in a cloud database.
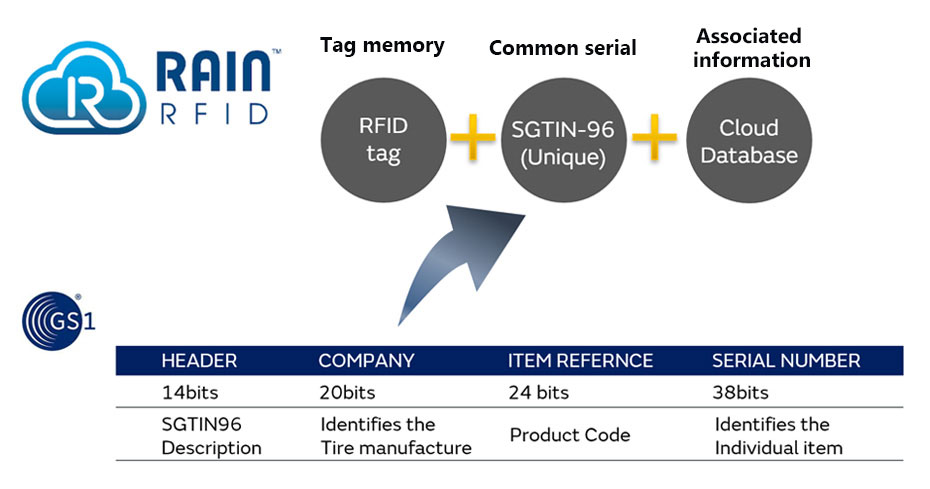
The establishment of Global Data Service Organization (GDSO)
The industry association was established for the purpose of collectively managing tires with different brands. The data associated with each tire ID (SGTIN-96) can be collectively managed in a database, divided between open and private data through good use of Web API.
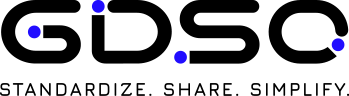
Using our own RFID software id-BridgeTM, we give demonstrations of RFID-based tire management using the GDSO system at MURATA MIRAI MOBILITY in our Minato MIRAI Innovation Center.
MURATA MIRAI MOBILITY
Image of Murata's RFID software id-BridgeTM in use
Please flick to see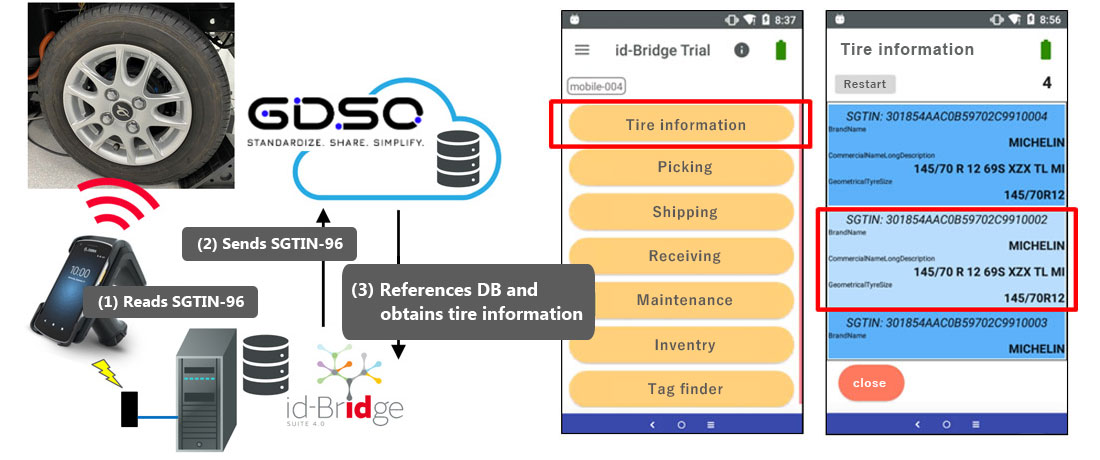
Tire-embeddable RFID tags achieving downsizing and robustness
Our tire-embeddable RFID tags, developed in coordination with Michelin, successfully overcame the reliability concern or issue, which conventional tire-embeddable RFID tags were facing, for their antenna connections through the breakthrough approach of having the RFID tags unequipped with any antenna. The high frequency and downsizing technologies that we have developed in the communications equipment market, as well as the technical insights we have acquired in the automobile market, are incorporated into our RFID modules serving as the key to the performance of our RFID tags.
Features
-
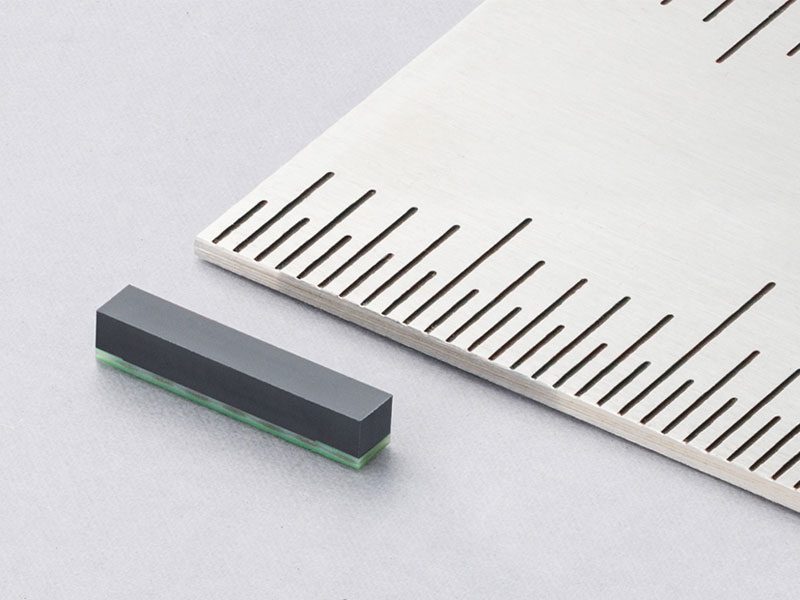
Downsizing of modules through our original technologies
Reducing module size while maintaining good electrical characteristics helps minimize impact on tires.
-

Successfully cleared a test of the loads expected during tire re-manufacturing/servicing processes and while on the road
The issue of conventional tire-embeddable RFID tags' antenna connections being easily breakable was solved through the adoption of a wireless charging system. Durability has been dramatically improved.
-

Designed so that the tag allows communication even after it is embedded in a tire
The RFID tag is designed bearing in mind the possible impact of the rubber and metals used in tires on its communication performance.
Our approach to embedding RFID tags in tires
To embed an RFID tag in a tire, it is necessary that the RFID tag be designed with consideration given to the rubber material and internal metals used for the tire and that enhanced communication characteristic evaluations be made on the RFID tag. Being rich in experience and knowledge of the communications equipment market, we can help with simulations of communication characteristics and tire evaluations.
-
STEP 01
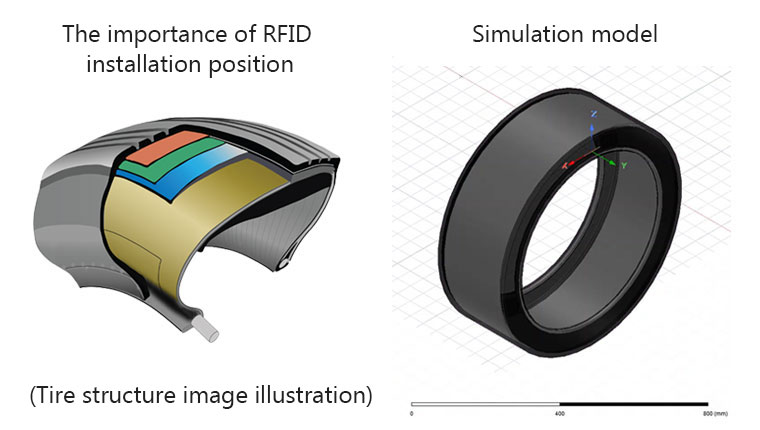
Creation of simulation models
It is possible to do a simulation of the electrical characteristics of an RFID tag and examine the reading performance of the RFID tag before embedding it into an actual tire. Based on such things as the overall diameter of the tire, the sizes and locations of its tire belts/bead wires and other metal materials, and the possible tag installation positions, a simulation model will be created.
-
STEP 02
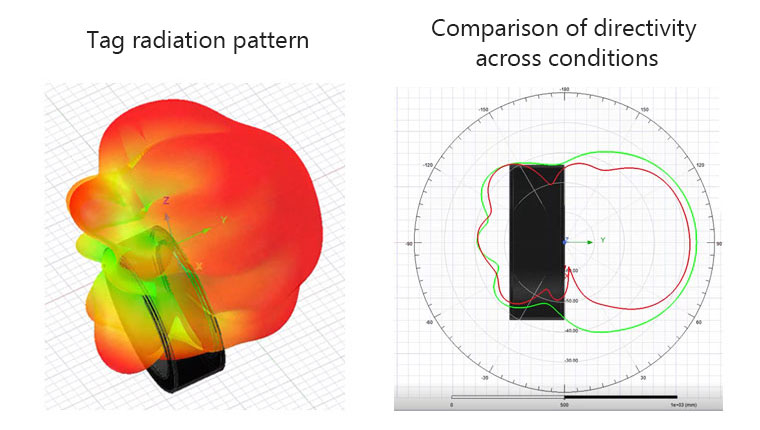
Reporting of simulation results
The reading distance and directivity (in which direction it is easy to read) of a tag can be determined from an electrical characteristic simulation. Performance comparisons of an RFID tag can be made under different conditions; so, before actually embedding the RFID tag into a tire, you can examine its possible installation positions or check the impact of variations in its installation position on its reading performance.
-
STEP 03
Embedding an RFID tag in a tire on your own
As we will provide you with an RFID tag sample, you should try to embed the RFID tag into a tire on your own.

-
STEP 04
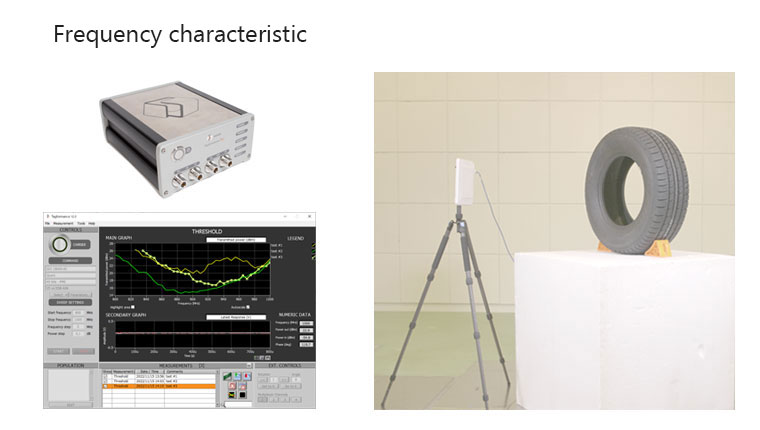
Support for the evaluation of measured reading performance
Using an anechoic chamber and an RFID tag performance inspection device, enhanced evaluations can be made of actual measurements of reading distances, frequency characteristics, etc.
Providing systems to support RFID implementation
We provide you with total support, offering a complete set of systems, including hardware, centered on our original RFID software id-BridgeTM. What is important to you at each tire manufacturing company is to do the following: tag encoding and warehousing using the GS1 SGTIN-96, and use of each tag ID (SGTIN-96) in the after-market to access tire product information and establish tag use cases (keeping track of incoming-outgoing shipments, inventory, inspection, disposal, etc.). The software id-BridgeTM is ready to evolve in pace with advances in tire business.

+

For customers looking for RFID tag/reader-writer.
Murata also offers hardwares from the lineup of RFID tag and reader-writer. Please find the detail in the product page.

